Primary E18 rat cortical neurons were enzymatically and mechanically dissociated and plated at low density on a monolayer of cortical astrocytes. Neuronal cultures were maintained with regular medium changes and recorded between 14–21 days in vitro, a timeframe selected to support stable synaptic receptor expression. Whole-cell voltage clamp electrophysiology was performed using standard instrumentation and acquisition software.
NMDA receptor–mediated currents were elicited by local puffer application of NMDA every 12 seconds following establishment of a stable baseline.
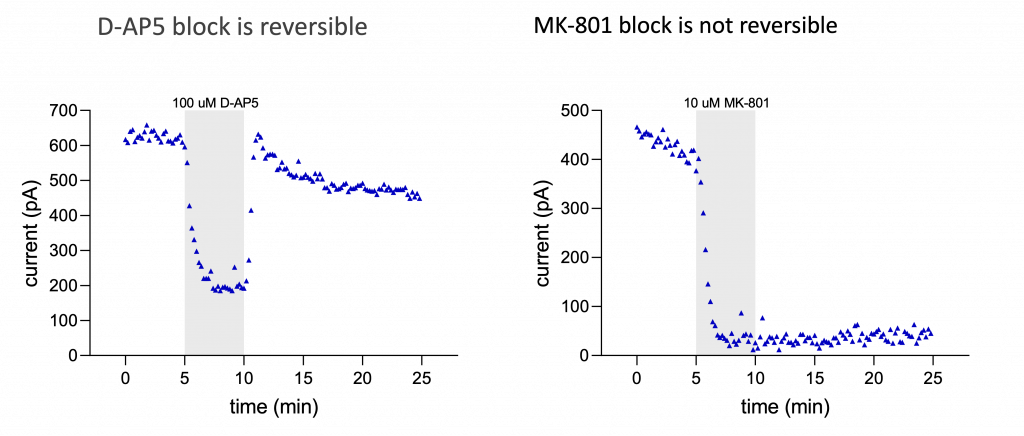
A) Reversible inhibition by D-AP5
B) Non-reversible inhibition by MK-801
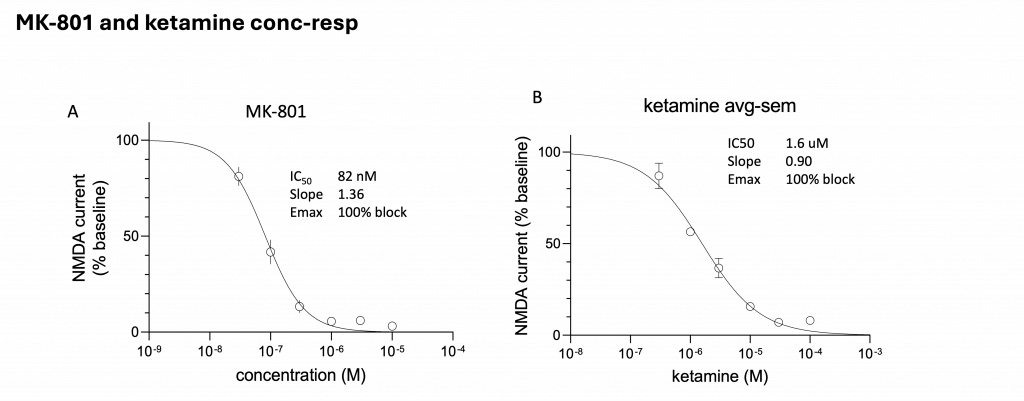
Concentration-dependent inhibition by A) MK-801 and B) ketamine
Using this study design, robust and reproducible NMDA receptor–mediated currents were recorded in rat cortical neurons. The assay successfully captured pharmacological modulation of NMDA currents, including:
These results confirm the suitability of this assay for quantitative evaluation of NMDA receptor pharmacology in primary neuronal cultures.